Introduction
The JC STEM Lab of MediaML @ HKU is at the forefront of this revolution, dedicated to pioneering research and development that enhances the intelligence and functionality of these service robots. Our lab’s primary focus revolves around the meticulous investigation of point cloud processing and analysis. This technology plays a pivotal role in helping robots perceive and understand their environment, laying the groundwork for more sophisticated and nuanced responses to external stimuli. By integrating multi-modality perception, we aim to elevate a robot’s sensory capabilities, making them more adept at navigating complex environments and scenarios. We are proud to collaborate with UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD, an established provider of smart service robotic solutions in mainland, as our strategic partner in this endeavor. This partnership not only enriches our research capacity but also fosters an environment of knowledge exchange, setting the stage for breakthrough innovations in the realm of service robotics.
Director: Professor Dong Xu
Our Research
Professor Dong Xu’s team at the University of Hong Kong will conduct research in the field of point cloud processing and analysis. Specifically, they will focus on one or more of the following research directions:
- Point Cloud Compression. Eficient and higtr-quality comprestion technicues are develoned for point cloud data. sienificantiy reducing storaze and bandwidth costs. This ncudes Geometry-haseoPoint Cloud Compression (G-PCC and Vide-based Point Cloud Compression (V-PCC),which are specifically designed for compressing point cloud data.
- Point Cloud Upsampling. Generate denser point clouds from sparse point clouds, including static point cloud upsampling and video-based point cloud upsampling.
- 3D Object Detection. 3D object detection is the process of detecting and categorizing objects of interest from 3D point cloud data, as well as estimating the position of their 3D bounding boxes.
- 3D Action Recognition. 3D action recognition is the process of identifying various human actions from sequences of 3D point cloud data.
- Model Compression. Model compression refers to the process of reducing the size and complexity of a pre-trained deep learning model to obtain a lightweight network with comparable accuracy. The compressed network has a smaller structure and fewer parameters, which effectively reduces computational and storage costs. This makes it easier to deploy the network in hardware-constrained environments.
- 3D Visual Grounding. The task of 3D visual grounding aims to address the following problem: determining the specific target object, including its category and the location of its 3D bounding box, through explicit and unambiguous language descriptions.
Publication
Point Cloud Compression
Authors: Zizheng Que, Guo Lu, Dong Xu
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a two-stage deep learning framework called VoxelContext-Net for both static and dynamic point cloud compression. Taking advantages of both octree based methods and voxel based schemes, our approach employs the voxel context to compress the octree structured data. Specifically, we first extract the local voxel representation that encodes the spatial neighbouring context information for each node in the constructed octree. Then, in the entropy coding stage, we propose a voxel context based deep entropy model to compress the symbols of non-leaf nodes in a lossless way. Furthermore, for dynamic point cloud compression, we additionally introduce the local voxel representations from the temporal neighbouring point clouds to exploit temporal dependency. More importantly, to alleviate the distortion from the octree construction procedure, we propose a voxel context based 3D coordinate refinement method to produce more accurate reconstructed point cloud at the decoder side, which is applicable to both static and dynamic point cloud compression. The comprehensive experiments on both static and dynamic point cloud benchmark datasets(e.g., ScanNet and Semantic KITTI) clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of our newly proposed method VoxelContext-Net for 3D point cloud geometry compression.
Our Method:
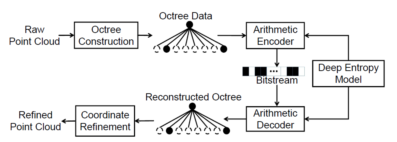
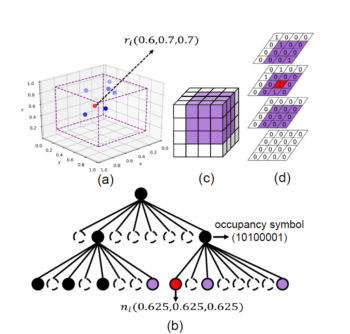
Reference: Z. Que*, G. Lu and D. Xu, “VoxelContext-Net: An Octree based Framework for Point Cloud Compression,” CVPR 2021
Point Cloud Upsampling
Authors: Kaisiyuan Wang, Lu Sheng, Shuhang Gu, Dong Xu
Abstract:In this work, we propose a new sequential point cloud upsampling method called SPU, which aims to upsample sparse, non-uniform, and orderless point cloud sequences by effectively exploiting rich and complementary temporal dependency from multiple inputs. Specifically, these inputs include a set of multi-scale short-term features from the 3D points in three consecutive frames (i.e., the previous/current/subsequent frame) and a long-term latent representation accumulated throughout the point cloud sequence. Considering that these temporal clues are not well aligned in the coordinate space, we propose a new temporal alignment module (TAM) based on the cross-attention mechanism to transform each individual feature into the feature space of the current frame. We also propose a new gating mechanism to learn the optimal weights for these transformed features, based on which the transformed features can be effectively aggregated as the final fused feature. The fused feature can be readily fed into the existing single frame-based point cloud upsampling methods (e.g., PU-Net, MPU and PU-GAN) to generate the dense point cloud for the current frame. Comprehensive experiments on three benchmark datasets DYNA, COMA, and MSR Action3D demonstrate the effectiveness of our method for upsampling point cloud sequences.
Our Method:
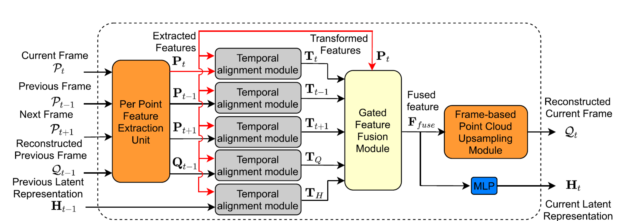
Reference: K. Wang*, L. Sheng, S. Gu and D. Xu, “Sequential Point Cloud Upsampling by Exploiting Multi-scale Temporal Dependency,” IEEE T-CSVT, 31(12), pp. 4686-4696, December 2021.
Authors: Kaisiyuan Wang, Lu Sheng, Shuhang Gu, Dong Xu
Abstract:In this work, we propose a new patch-based framework called VPU for the video-based point cloud upsampling task by effectively exploiting temporal dependency among multiple consecutive point cloud frames, in which each frame consists of a set of unordered, sparse and irregular 3D points. Rather than adopting the sophisticated motion estimation strategy in video analysis, we propose a new spatio-temporal aggregation (STA) module to effectively extract , align and aggregate rich local geometric clues from consecutive frames at the feature level. By more reliably summarizing spatio-temporally consistent and complementary knowledge from multiple frames in the resultant local structural features, our method better infers the local geometry distributions at the current frame. In addition, our STA module can be readily incorporated with various existing single frame-based point upsampling methods ( e.g. , PU-Net, MPU, PU-GAN and PU-GCN). Comprehensive experiments on multiple point cloud sequence datasets demonstrate our video-based point cloud upsampling framework achieves substantial performance improvement over its single frame-based counterparts.
Our Method:
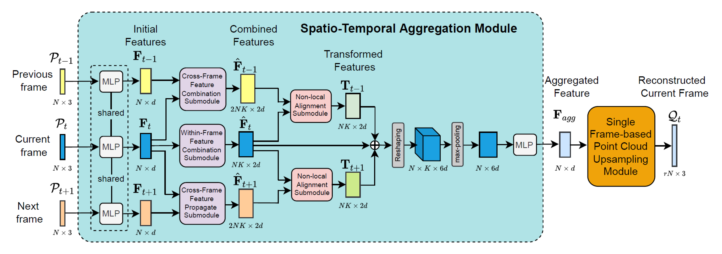
Reference: K. Wang*, L. Sheng, S. Gu and D. Xu, “VPU-Net: A Video-based Point Cloud Upsampling Framework,” IEEE T-IP, 31, pp. 4062-4075, 2022.
3D Object Detection
Authors: Weichen Zhang, Wen Li, Dong Xu
Abstract:Geometric characteristic plays an important role in the representation of an object in 3D point clouds. For example, large objects often contain more points, while small ones contain fewer points. The point clouds of objects near the capture device are denser, while those of distant objects are sparser. These issues bring new challenges to 3D object detection, especially under the domain adaptation scenarios. In this work, we propose a new cross-dataset 3D object detection method named Scale-aware and Range-aware Domain Adaptation Network (SRDAN). We take advantage of the geometric characteristics of 3D data (i.e., size and distance), and propose the scale-aware domain alignment and the range-aware domain alignment strategies to guide the distribution alignment between two domains. For scale-aware domain alignment, we design a 3D voxel-based feature pyramid network to extract multi-scale semantic voxel features, and align the features and instances with similar scales between two domains. For range-aware domain alignment, we introduce a range-guided domain alignment module to align the features of objects according to their distance to the capture device. Extensive experiments under three different scenarios demonstrate the effectiveness of our SRDAN approach, and comprehensive ablation study also validates the importance of geometric characteristics for cross-dataset 3D object detection.
Our Method:

Reference: W. Zhang*, W. Li and D. Xu, “SRDAN: Scale-aware and Range-aware Domain Adaptation Network for Cross-dataset 3D Object Detection,” CVPR, June 2021.
Authors: Bowen Cheng, Lu Sheng, Shaoshuai Shi, Ming Yang, Dong Xu
Abstract:3D object detection in point clouds is a challenging vision task that benefits various applications for understanding the 3D visual world. Lots of recent research focuses on how to exploit end-to-end trainable Hough voting for generating object proposals. However, the current voting strategy can only receive partial votes from the surfaces of potential objects together with severe outlier votes from the cluttered backgrounds, which hampers full utilization of the information from the input point clouds. Inspired by the back-tracing strategy in the conventional Hough voting methods, in this work, we introduce a new 3D object detection method, named as Back-tracing Representative Points Network (BRNet), which generatively back-traces the representative points from the vote centers and also revisits complementary seed points around these generated points, so as to better capture the fine local structural features surrounding the potential objects from the raw point clouds. Therefore, this bottom-up and then top-down strategy in our BRNet enforces mutual consistency between the predicted vote centers and the raw surface points and thus achieves more reliable and flexible object localization and class prediction results. Our BRNet is simple but effective, which significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on two large-scale point cloud datasets, ScanNet V2 (+7.5% in terms of mAP@0.50) and SUN RGB-D (+4.7% in terms of mAP@0.50), while it is still lightweight and efficient.
Our Method:
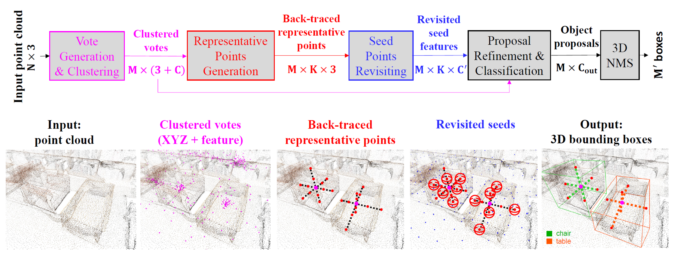
Reference: B. Chen, L. Sheng, M. Yang, S. Shi and D. Xu, “Back-tracing Representative Points for Voting-based 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds,” CVPR, June 2021.
Authors: Lichen Zhao, Jinyang Guo, Dong Xu, Lu Sheng
Abstract:Voting-based methods (e.g., VoteNet) have achieved promising results for 3D object detection. However, the simple voting operation in VoteNet may lead to less accurate voting results that are far away from the true object centers. In this work, we propose a simple but effective 3D object detection method called Transformer3D-Det (T3D), in which we additionally introduce a transformer based vote refinement module to refine the voting results of VoteNet and can thus significantly improve the 3D object detection performance. Specifically, our T3D framework consists of three modules: a vote generation module, a vote refinement module, and a bounding box generation module. Given an input point cloud, we first utilize the vote generation module to generate multiple coarse vote clusters. Then, the clustered coarse votes will be refined by using our transformer based vote refinement module to produce more accurate and meaningful votes. Finally, the bounding box generation module takes the refined vote clusters as the input and generates the final detection result for the input point cloud. To alleviate the impact of inaccurate votes, we also propose a new non-vote loss function to train our T3D. As a result, our T3D framework can achieve better 3D object detection performance. Comprehensive experiments on two benchmark datasets ScanNetV2 and SUN RGB-D demonstrate the effectiveness of our T3D framework for 3D object detection.
Our Method:
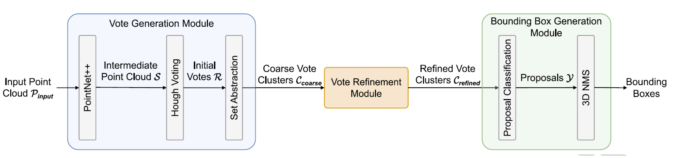
Reference: L. Zhao*, J. Guo*, D. Xu and L. Sheng, “Transformer3D-Det: Improving 3D Object Detection by Vote Refinement,” IEEE T-CSVT, 31(12), pp. 4735-4746, December 2021.
3D Action Recognition
Authors: Jiaheng Liu, Jinyang Guo, Dong Xu
Abstract:Observing that it is still a challenging task to deploy 3D action recognition methods in real-world scenarios, in this work, we investigate the accuracy-efficiency trade-off for 3D action recognition. We first introduce a simple and efficient backbone network structure for 3D action recognition, in which we directly extract the geometry and motion representations from the raw point cloud videos through a set of simple operations ( i.e., coordinate offset generation and mini-PoinNet). Based on the backbone network, we propose an end-to-end optimized network called adaptive point sampling network (APSNet) to achieve the accuracy-efficiency trade-off, which mainly consists of three stages: the coarse feature extraction stage, the decision making stage, and the fine feature extraction stage. In APSNet, we adaptively decide the optimal resolutions ( i.e., the optimal number of points) for each pair of frames based on any input point cloud video under the given computational complexity constraint. Comprehensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our newly proposed APSNet for 3D action recognition.
Our Method:

Reference: J. Liu*, J. Guo* and D. Xu, “APSNet: Towards Adaptive Point Sampling for Efficient 3D Action Recognition,” T-IP, 31, pp. 5287-5302, 2022.
Authors: Jiaheng Liu, Jinyang Guo, Dong Xu
Abstract:In this work, we propose a new end-to-end optimized two-stream framework called GeometryMotion-Transformer (GMT) for 3D action recognition. We first observe that the existing 3D action recognition approaches cannot well extract motion representations from point cloud sequences. Specifically, when extracting motion representations, the existing approaches do not explicitly consider one-to-one correspondence among frames. Besides, the existing methods only extract the single-scale motion representations, which cannot well model the complex motion patterns of moving objects in point cloud sequences. To address these issues, we first propose the feature extraction module (FEM) to generate one-to-one correspondence among frames without using the voxelization process, and explicitly extract both geometry and multi-scale motion representations from raw point clouds. Moreover, we also observe the existing two-stream 3D action recognition approaches simply concatenate or add the geometry and motion features, which cannot well exploit the relationship between two-steam features. To this end, we also propose an improved transformer-based feature fusion module (FFM) to effectively fuse the two-stream features. Based on the proposed FEM and FFM, we build our GMT for 3D action recognition. Extensive experimental results on four benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our backbone GMT.
Our Method:
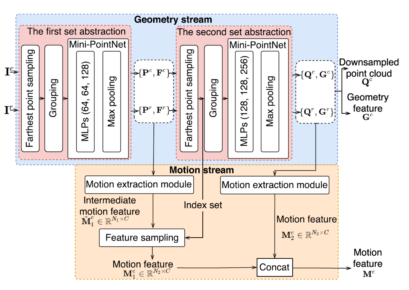
Reference: J. Liu*, J. Guo* and D. Xu, “GeometryMotion-Transformer: An End-to-End Framework for 3D Action Recognition,” T-MM, Accepted (In Press).
Authors: Jiaheng Liu, Dong Xu
Abstract:In this work, we propose a strong two-stream baseline method referred to as GeometryMotion-Net for 3D action recognition. For efficient 3D action recognition, we first represent each point cloud sequence as a limited number of randomly sampled frames with each frame consisting of a sparse set of points. After that, we propose a new two-stream framework for effective 3D action recognition. For the geometry stream, we propose a new module to produce a virtual overall geometry point cloud by first merging all 3D points from these selected frames, and then we exploit local neighborhood information of each point in the feature space. In the motion stream, for any two neighboring point cloud frames, we also propose a new module to generate one virtual forward motion point cloud and one virtual backward motion point cloud. Specifically, for each point in the current frame, we first produce a set of 3D offset features relative to the neighboring points in the reference frame ( i.e. , the previous/subsequent frame) and then exploit local neighborhood information of this point in the offset feature space. Based on the newly generated virtual overall geometry point cloud and multiple virtual forward/backward motion point clouds, any existing point cloud analysis methods ( e.g. , PointNet) can be readily adopted for extracting discriminant geometry and bidirectional motion features in the geometry and motion streams, respectively, which are further aggregated to make our two-stream network trainable in an end-to-end fashion. Comprehensive experiments on both large-scale datasets ( i.e. NTU RGB+D 60 and NTU RGB+D 120) and small-scale datasets ( i.e. , N-UCLA and UWA3DII) demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our two-stream network for 3D action recognition.
Our Method:
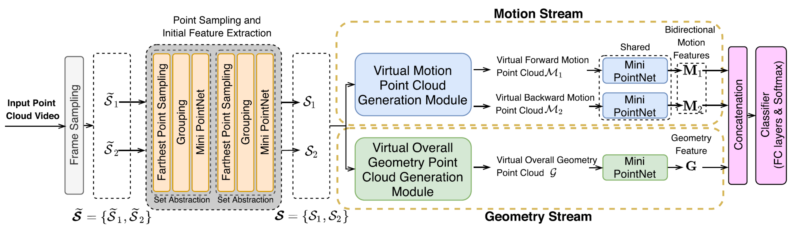
Reference:J. Liu* and D. Xu, “GeometryMotion-Net: A Strong Two-stream Baseline for 3D Action Recognition,” T-CSVT, 31(12), pp. 4711-4721, December 2021.
Model Compression
Authors: Jinyang Guo, Jiaheng Liu, Dong Xu
Abstract:Deep neural networks designed for point clouds, also called point cloud neural networks (PCNNs), are attracting increasing attention in recent years. In this work, we propose the first model compression framework referred to as JointPruning (JP) that is specifically designed for compressing PCNNs. Observing that the redundancies in PCNNs are largely affected by certain parameters like the number of points, we first propose a new search space specifically designed for PCNNs. By searching the optimal pruning policy in our newly proposed search space, our JP framework can prune the PCNNs at different levels and simultaneously reduce the redundancies along multiple dimensions. As the newly proposed search space consists of multiple levels and the policy value at each level is continuous in our JP framework, it is hard to directly search for the best pruning policy in such a large search space. To this end, we further propose two strategies called search space refinement and validation set extension to progressively refine the granularity of our searching process in a coarse-to-fine and easy-to-hard fashion, which can help us gradually find better pruning policies. Comprehensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our JP framework for compressing PCNNs.
Our Method:
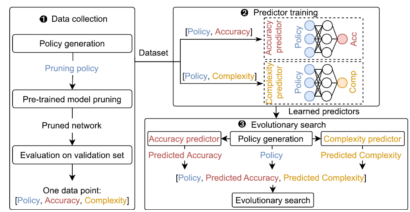
Reference:J. Guo*, J. Liu* and D. Xu, “JointPruning: Pruning Networks along Multiple Dimensions for Efficient Point Cloud Processing,” IEEE T-CSVT, 32(6), pp. 3659-3672, June 2022.
Authors: Jinyang Guo, Jiaheng Liu, Dong Xu
Abstract:The existing end-to-end optimized 3D action recognition methods often suffer from high computational costs. Observing that different frames and different points in point cloud sequences often have different importance values for the 3D action recognition task, in this work, we propose a fully automatic model compression framework called 3D-Pruning (3DP) for efficient 3D action recognition. After performing model compression by using our 3DP framework, the compressed model can process different frames and different points in each frame by using different computational complexities based on their importance values, in which both the importance value and computational complexity for each frame/point can be automatically learned. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our 3DP framework for model compression.
Our Method:
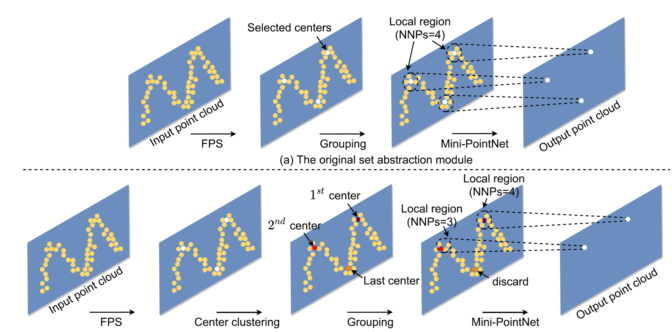
Reference:J. Guo*, J. Liu* and D. Xu, “3D-Pruning: A Model Compression Framework for Efficient 3D Action Recognition,” IEEE T-CSVT, Accepted (In Press).
3D Visual Grounding
Authors: Lichen Zhao, Daigang Cai, Lu Sheng, Dong Xu
Abstract:Visual grounding on 3D point clouds is an emerging vision and language task that benefits various applications in understanding the 3D visual world. By formulating this task as a grounding-by-detection problem, lots of recent works focus on how to exploit more powerful detectors and comprehensive language features, but (1) how to model complex relations for generating context-aware object proposals and (2) how to leverage proposal relations to distinguish the true target object from similar proposals are not fully studied yet. Inspired by the well-known transformer architecture, we propose a relation-aware visual grounding method on 3D point clouds, named as 3DVG-Transformer, to fully utilize the contextual clues for relation-enhanced proposal generation and cross-modal proposal disambiguation, which are enabled by a newly designed coordinate-guided contextual aggregation (CCA) module in the object proposal generation stage, and a multiplex attention (MA) module in the cross-modal feature fusion stage. We validate that our 3DVG-Transformer outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by a large margin, on two point cloud-based visual grounding datasets, ScanRefer and Nr3D/Sr3D from ReferIt3D, especially for complex scenarios containing multiple objects of the same category.
Our Method:
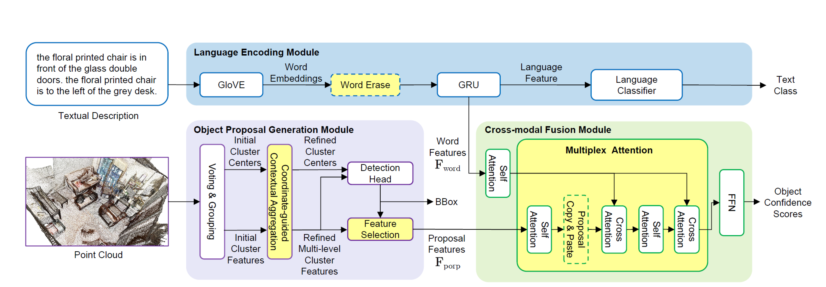
Reference:L. Zhao*, D. Cai*, L. Sheng and D. Xu, “3DVG-Transformer: Relation Modeling for Visual Grounding on Point Clouds,” ICCV, October 2021.
Authors: Daigang Cai, Lichen Zhao, Jing Zhang, Lu Sheng, Dong Xu
Abstract:Observing that the 3D captioning task and the 3D grounding task contain both shared and complementary information in nature, in this work, we propose a unified framework to jointly solve these two distinct but closely related tasks in a synergistic fashion, which consists of both shared task-agnostic modules and lightweight task-specific modules. On one hand, the shared task-agnostic modules aim to learn precise locations of objects, fine-grained attribute features to characterize different objects, and complex relations between objects, which benefit both captioning and visual grounding. On the other hand, by casting each of the two tasks as the proxy task of another one, the lightweight task-specific modules solve the captioning task and the grounding task respectively. Extensive experiments and ablation study on three 3D vision and language datasets demonstrate that our joint training frame-work achieves significant performance gains for each individual task and finally improves the state-of-the-art performance for both captioning and grounding tasks.
Our Method:
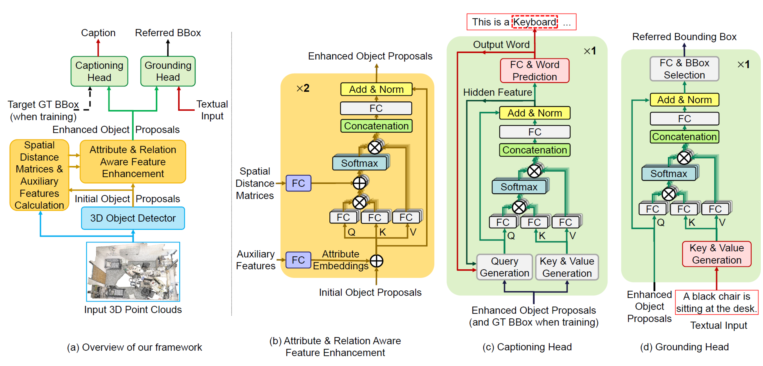
Reference:D. Cai*, L. Zhao*, J. Zhang, L. Sheng and D. Xu, “3DJCG: A Unified Framework for Joint Dense Captioning and Visual Grounding on 3D Point Clouds,” CVPR, June 2022. (Oral)
